CAUSES OF ORTHOSIS
1.Preventing deformity
2.Correcting soft tissue deformities
3.Protecting weak muscles
4.To control deviations caused by tonus disorder
5.Improving patients’ standing upright with biomechanical supports and facilitating independent walking
Evaluation of Orthosis
The orthotic target
The neurological picture of the patient and the level of deficits,
Voluntary muscles control
Static and dynamic joint range of motion
Dynamic and fixation deformity
Spasticity
Age
Mental status
Orthoses Used in Cerebral Palsy
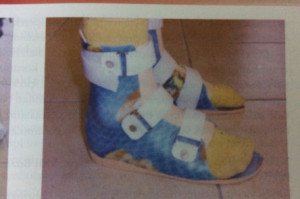
Rest PAFO (plastic foot/ankle orthosis)
It aims to keep the ankles of children with SP in a 90° neutral position due to spasticity in thecalf muscles. It is usually used in cases where the plantar flexor spasticity or dorsiflexor muscles do not work for 8-10 hours.

In general, it should have the following characteristics:
- Subtalar should keep the joint in neutral
- The heel part should be partially rounded and curved
- Medial-longitudinal arch should not be kept high
- Should be perforated or thin material
- Fulfill the function, wrap the foot and fit properly
- It should not have a place that hurts and hits
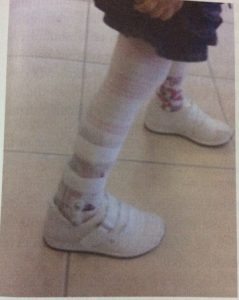
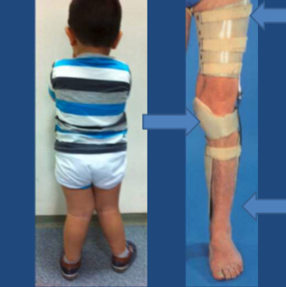
PCAFO ( plastic knee, foot, ankle orthosis)
It is used to keep the knees straight in children walking in the non-ambulatory and crouch gait positions with severe flexor spasticity.

It is used in KAFOSP for standing upright orambulatory purposes.
- To support weak muscles after multiple level lower extremity operations,
- Protecting the EHA,
- increase knee extension in posture or gait,
- controlling hyperextension
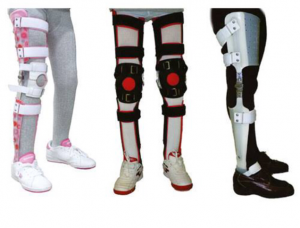
HKAFO is a body-supported gaiter in which children withhypotonic muscles are tried to be kept standing. It involves thehip joint.Innon-ambulatory children, it is aimed to maintain the range of motion of the hip joint and to reduce the risk of subluxation and dislocation.

FO
They do not provide effective plantar flexion and dorsiflexion control in the ankle!!
They are generally used to regulate and maintain the forefoot, middle foot and hindfoot segment in the presence of deformities such as planovalgus/varicose veins standing in hypotonic children. They are examined in 2 groups according to their height.
1- Inframalleolar Orthoses: They are used to control moderate PES planovalgus deformity in children with hypotonic or ataxic SP.
2- Supramalleoler: Includes malleoles. Areas where it is frequently used;
- Mediolateral instability of subtalar joints
- Midfoot instability leading to varus/valgus deformity in the forefoot,
- Reduction of mild to moderate spasticity and hypertonic reflex activity
The articulated AFO is functional dorsiflexion free plans are formed in the knee joint in the push phase with push-stop and a good QF muscle strength is required to meet this. Otherwise, the patient loses knee control while walking.
DAFO (Dynamic AFO) provides support forthin, flexible, dynamic arcs, stabilization mediolateral
control, while allowing different degrees of DF and PF movements in the ankle.
It is thought to reduce abnormal PF movement and inhibit hypertonus thanks to mediolateral stability.GRAFO (Place reaction orthosis)
GRAPHO (Ground reaction orthosis)
Closed from the front
It prevents the tibia from being displaced forward during posture and creates the extensor moment that should be created by the QF muscles.
It is used in the case when there is a bent knee gait in children with SP.
>it should not be used in cases where there is a 10° hip and knee flexion contracture!!!
In the presence of genu recurvatum, it rises above the knee joint and creates a flexor moment.

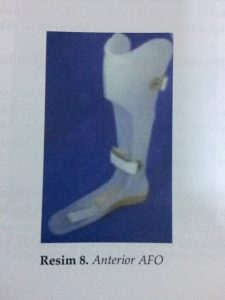
Anterior AFO:
It aims to keep the ankle at 90° by wrapping the leg in front and prevent knee flexion by controlling the forward movement of the tibia.
It is used in cases of ankle muscles weakness.
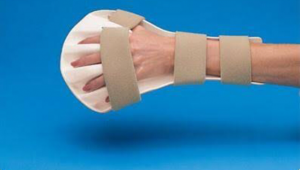
Inhibitory Hand Splints
They are total contact orthoses in which the thumb is held in position at 20°-25° extension of the wrist and the other fingers are held in abduction.
It is often used as a night orthosis.
It should be noted that with orthoses of the upper extremities, the orthosis should not cover the volar face of the palm and fingers.
Orthoses Used in Neuromuscular Diseases
PAFO
Orthosis should not be recommended in the ambulatory period in DMD patients!
However, in order to prevent the ankle position from becoming permanent in this plantar flexion, a fixed PAFO is used that holds the ankle at 90°.
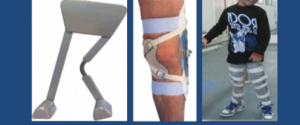
In muscle diseases, CAFOs and long walking devices are used in cases where the QF muscle cannot lock the patient’s knee in partial/full strength loss. KAFO should be usedespecially when the ability to walk in DMD starts to disappear. When thepatient is unable to walk, body corset may need to be added to the CAFO according to the muscle strength of the body. For this purpose, bilateral polyethylene long-walking orthoses connected to the corset, which are also used for verticalization and subsequent gait of children with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) who cannot stand independently, are frequently recommended.
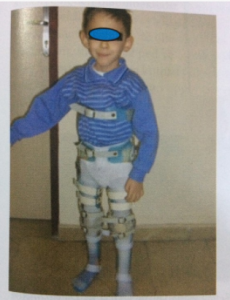
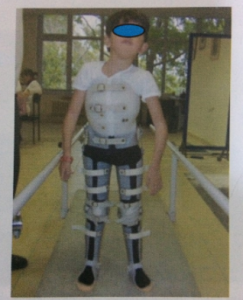
Points to check on the long walking device:
Are there asymmetries and protrusions in theside bars?
Do all the mechanical joints from distal to proximal match the anatomical joints?
If there is a pelvic arch, it should be checked.
The patient is asked to open and close the locks and training is given.
Afteruse, it should be checked and if necessary, modifications should be made
Scoliosis
CorsetPurpose; Slowing the curve progression rate, supporting the spine until surgery, preventing body collapse, ensuring independent sitting.
In this orthosis, the anterior parts should be opened for respiratory continuity.Respiratory exercises
should be taught!!!

Orthoses Used in Congenital or Acquired Problems
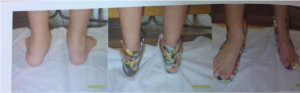
Pes Planus /Pes Planovalgus
Pes planus:
Suitable shoes /insoles when necessary ( MLA supports )
If the posterior foot valve is also accompanied, medial heel wedge, calcaneal cup and UCBL orthosis
Pes Equinivarus:
Dennis Browne orthosis
In many treatment protocols, orthosis is recommended, which positions the leg and foot in a 70° external rotation until the child walks.

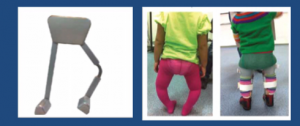
Genu Varum/ Valgum
Wedge insoles
3-point principle
Constant KAFO
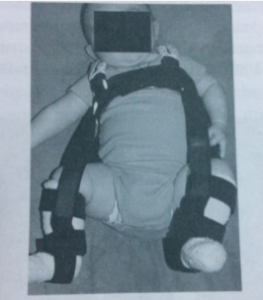
Developmental Hip Dysplasia
• Pavlik Harnes
• Frejka pillow
• Hip abduction orthosis
• Ponsetti
• 3months, an additional 6 months if dislocation is detected
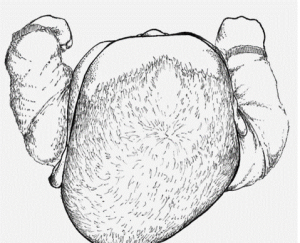
Torticollis
Flexible
Helmet in cases whereskull asymmetry develops


Leave a Reply